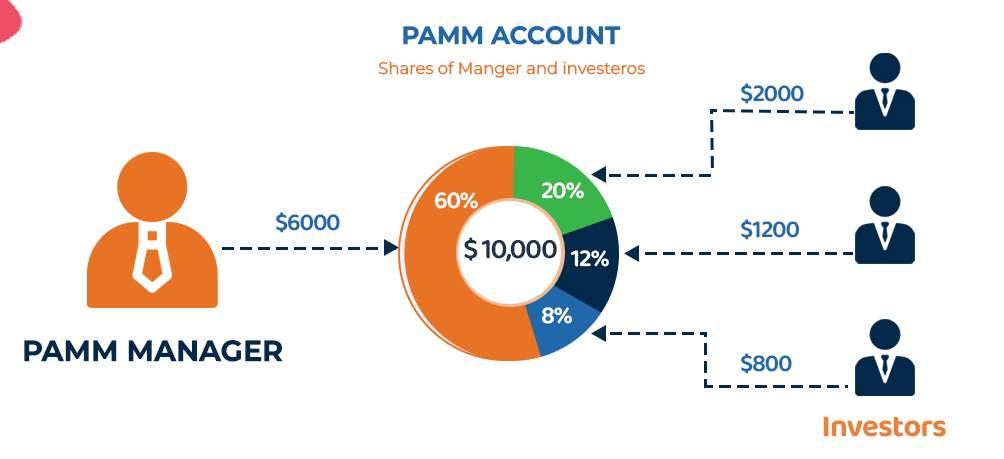
US Federal Reserve plans to raise interest rates from March to ease inflation
Behave as instantaneously demanding situations for the threat urge for food and the USD/JPY pair.
“Japan`s each day remember of latest COVID-19 instances hit but any other report of over 70,000 on Wednesday because the extra transmissible Omicron variation keeps its fast unfold in Tokyo and elsewhere,” stated Kyodo News.
Talking approximately the information, US housing numbers progressed in December while Japan`s Foreign Bond Investment contracted to bad and the Foreign Investment in Japan Stocks reversed the preceding contraction with ¥10.2B level.
Against this backdrop, US equities and commodities remained at the lower back foot, besides for oil, while the United States 10-yr Treasury yields rose the maximum in 3 weeks, up 8 foundation points (bps) to 1.87% with the aid of using the quit of Wednesday`s North American session. That stated, the UThe Federal Reserve signaled on January 26, 2022, that it will begin a series of rate hikes in March, reversing pandemic policies that have boosted hiring and growth – and stock market returns – but inflation is also high.
Chairman Jerome Powell said in a news conference that inflation has “worsened a bit” since the Fed’s last meeting in December. He said the Fed’s benchmark interest rate hike, which has been set at 0 as of March 2020, will help prevent high prices.
Seeking to allay concerns that higher rates could hurt the economy, Powell said the central bank can manage the process in a way that prolongs growth and keeps unemployment low. . “I think there is enough room to raise rates without threatening the labor market,” he said. Economists say they are surprised at the likely duration and intensity of a rate hike by Powell, who said the economy is now stronger than it was in 2015, when the Fed began to slowly increase interest rate. “The Fed is signaling that it will act sooner, and perhaps at a faster pace than we thought,” said Steve Rick, chief economist at CUNA Mutual Group.
Fed rate hikes will make it more expensive to buy a home, car or business over time. The Fed’s intention is to rein in economic growth and soften inflation, which is at a 40-year high and is eating away at US wage growth and household budgets. “The best thing we can do to support the continued strength of the labor market,” said Powell, “is to foster long-term expansion, and that will require price stability.”
The central bank’s latest policy statement comes after wild swings in the stock market as investors were gripped by fear and uncertainty about the Fed going against course. how quickly and how far low interest rate policy has boosted the economy and markets for years. The broad S&P 500 index has fallen nearly 10% this month and was lower on January 26, 2022.
When asked about the stock market volatility, Powell indicated that “the last focus is on the bottom line.” The end” of the Fed is the “real economy”. But he sees recent market moves as a positive sign: “We feel like the communications we have with market participants and the general public are working.” High inflation has become a serious political threat to President Joe Biden and congressional Democrats, with Republicans seeing rising prices as one of their main attacks. as they head towards the November election,
Biden last week said it was “appropriate” for Powell to adjust Fed policies and Republicans have endorsed Powell’s plan to raise rates, providing the Fed with rare bipartisan support for tightening credit. “Risks are accelerating the pace of Fed tightening as inflation persists,” said Kathy Bostjancic, an economist at consulting firm Oxford Economics.
Supply chain and labor market constraints have lasted longer than the Fed expected. Consumer prices are rising 7% – well above the Fed’s long-term inflation target of 2% – and Powell said the outlook for the US economy remains uncertain.
Powell says that while he thinks bottlenecks and labor constraints will ease over time, it’s important for Fed policymakers to show “humility” and “agility.” in their decision-making.
For now, Powell said Fed policymakers are “one of those looking to raise lending rates at the March meeting, assuming conditions are right starting in July. Powell and the Fed have been “very, very clear that a rate hike is imminent, the scope for a rate hike is large, and they’re moving fast toward shrinking the Fed’s balance sheet,” said Eric Winograd, economist American economist at AB, an asset manager. Central banks are faced with a delicate, even risky balancing act. If the stock market sinks into more chaotic declines, the Fed may decide to delay some of its credit-tightening plans, economists say. Still, the modest drop in stock prices is unlikely to sway the Fed’s thinking.
Some economists expressed concern that the Fed was acting too late to combat high inflation. Others say they fear the Fed is acting too aggressively. They argue that multiple rate hikes could unnecessarily slow down hiring. From this perspective, high prices primarily reflect a troubled supply chain that a Fed rate hike is unlikely to fix.
Powell admits that he did not anticipate the prolongation of high inflation, having long expressed confidence that it would only be temporary. The spike in inflation has spread to areas beyond those affected by supply shortages – apartment rents, for example – suggesting it can persist even after goods and parts freer circulation.