Understanding Forex Spreads: Definition, Types, and Calculation
In forex trading, understanding spreads is essential for maximizing profitability. This guide explores what forex spreads are, how they function, and how to calculate and monitor them effectively.
What is a Spread in Forex?
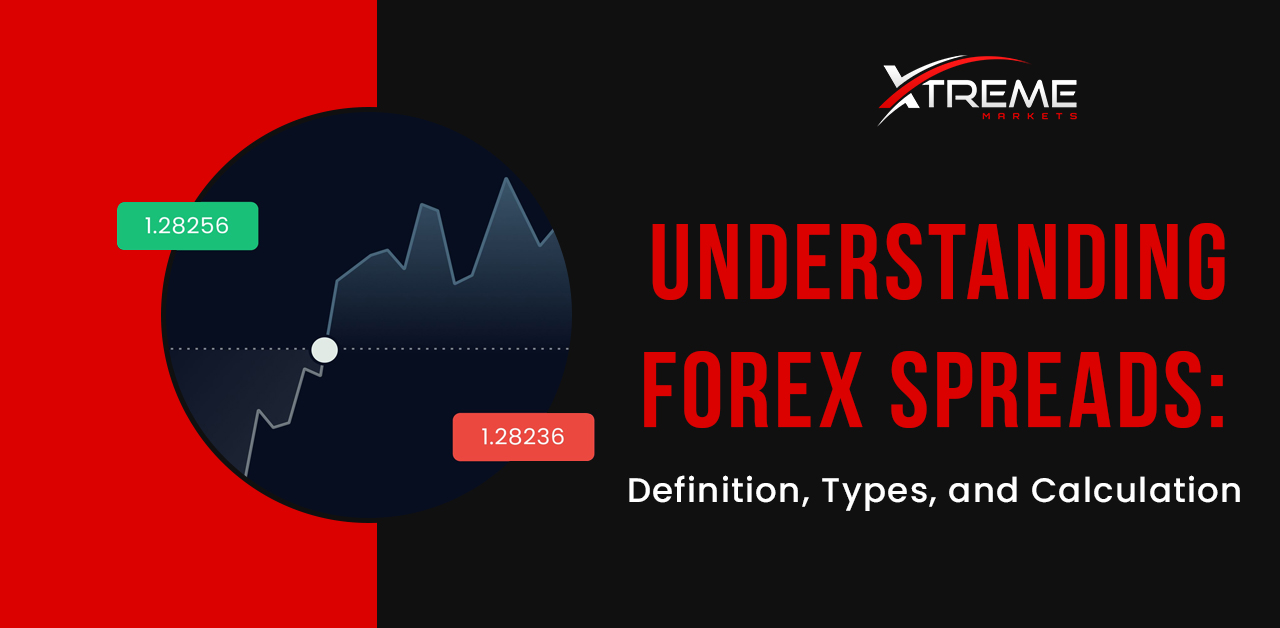
In forex, the spread is the difference between the ask price and the bid price of a currency pair. Spread size depends on factors such as market volatility and the currency pairs being traded. During volatile periods, spreads widen, increasing transaction costs.
Types of Forex Spreads
The choice between several types of spreads is the key consideration for traders when it comes to online forex trading. Following are the two main two types of spreads:
1. Fixed Spreads
Fixed spreads are pre-set and do not fluctuate with market conditions. They offer both advantages and disadvantages:
- Pros: Traders know the exact spread in advance, which helps with planning and risk management. Fixed spreads are stable, providing predictability even during market volatility.
- Cons: Fixed spreads are often higher than variable ones, as brokers factor in their profit margin. Fixed spreads may also have limited liquidity, potentially causing slippage and delayed trade execution, especially in high-volume trades.
- Variable (Floating) Spreads
Variable spreads fluctuate based on market conditions and are typically offered by brokers connected to the interbank market through ECN (Electronic Communication Network) or STP (Straight-Through Processing).
- Pros: Variable spreads are usually narrower under normal conditions, reducing trading costs, especially for high-volume traders. They also offer real-time pricing, allowing a more transparent view of bid-ask prices.
- Cons: During high volatility, variable spreads can widen significantly, increasing trading costs. Brokers offering variable spreads may experience slippage during low liquidity, potentially impacting trader profits.
Calculating Forex Spreads
To calculate the spread, you need the ask and bid prices:
- Ask Price: The lowest price at which a currency can be sold.
- Bid Price: The highest price a trader is willing to pay for a currency.
The formula for calculating the spread as a percentage is:
Spread (%)=(Ask Price−Bid PriceAsk Price)×100\text{Spread (\%)} = \left( \frac{\text{Ask Price} – \text{Bid Price}}{\text{Ask Price}} \right) \times 100Spread (%)=(Ask PriceAsk Price−Bid Price)×100
Factors Affecting Forex Spreads
- Liquidity: Higher liquidity usually results in tighter spreads, while low liquidity widens them.
- Volatility: Economic events or news can create high volatility, widening spreads as exchange rates fluctuate rapidly.
- Time of Day: Trading during peak times (e.g., London-New York overlap) increases liquidity and narrows spreads, while off-hours may see wider spreads.
Importance of Understanding Forex Spreads
- Impact on Trading Costs: The impact of spreads on trading costs is significant, as a wider spread implies a higher cost for entering and exiting positions. Traders aim to profit from price fluctuations, and the spread immediately affects their ability to do so. A larger spread means that the market must move more in favour of the trader before they can break even or make a profit. Consequently, traders often seek brokers offering tighter spreads to minimize their trading cost.
- Risk Management: As spreads have a direct impact on the cost of trading and risk management strategies, it is important to understand the concept thoroughly. When traders can accurately determine spreads, they are able to calculate potential profits in a better way. This implies that the traders can start closer to breakeven, minimizing the need for price movements to be in their favour. In turn, this enhances risk management by allowing for smaller stop-loss orders and reducing the risk of slippage, helping traders make more informed and cost-effective trading decisions.
Tips for Minimizing Spread Costs
- Choose the Right Broker: Finding a broker that offers competitive spreads and minimal commissions is essential because trading costs significantly impact the profitability of the traders. The broker must stand out in terms of offering competitive pricing for forex trading. The broker must guarantee the traders that they can execute their transactions at the best rates, boosting their potential profits, with tight spreads and open commission structures.
- Trade During Optimal Times: For optimal trading, choose hours with narrow spreads, usually during market overlaps. The best times include London-New York overlap (8 am to 12 pm EST) and London-Tokyo overlap (3 am to 4 am EST). These periods maximize liquidity, reducing spreads, and providing more favorable conditions for traders.
Conclusion
Understanding forex spreads and knowing when to trade can help manage costs and improve trading outcomes. By trading during high-liquidity periods, using limit orders, and staying informed about market events, traders can navigate spreads effectively to achieve their goals.
Ready to Start Forex Trading?
Test your skills and knowledge in the market with XtremeMarkets.