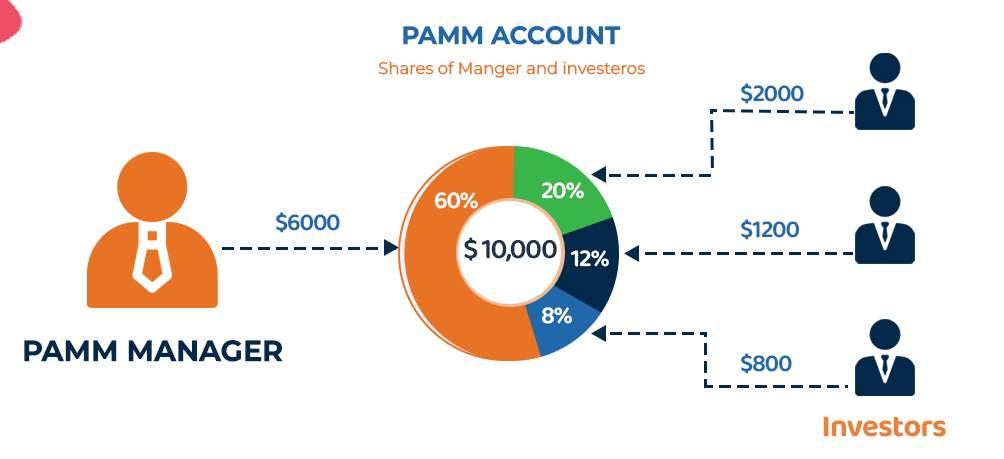
Fed’s Bowman Stresses Prematurity of Interest Rate Cuts
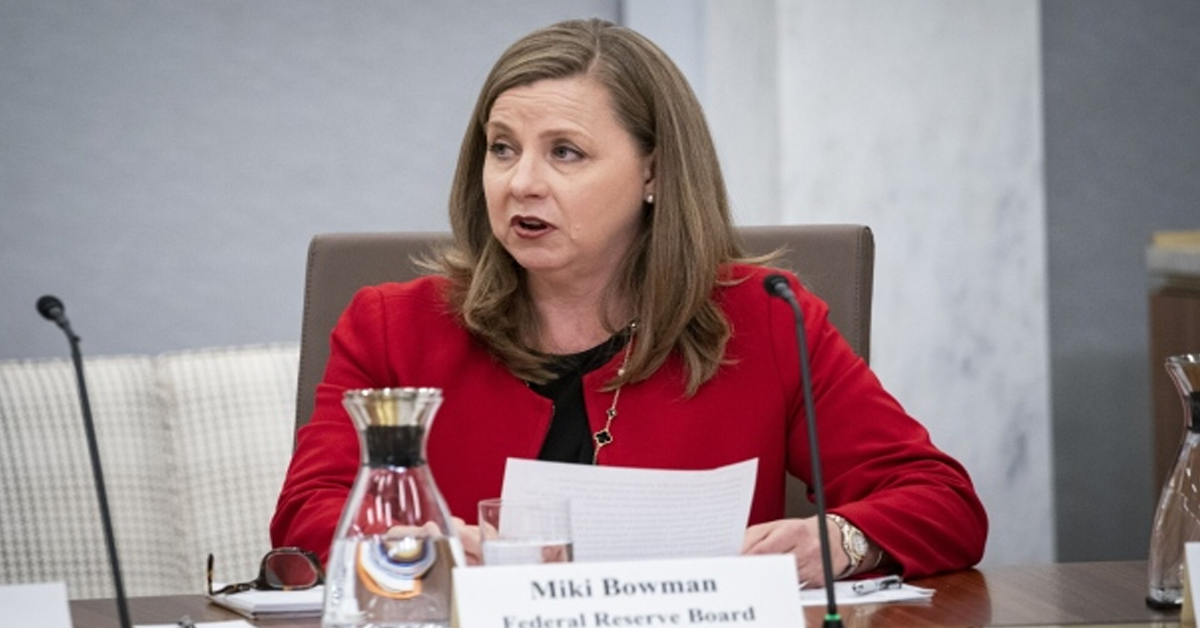
Federal Reserve Governor Michelle Bowman recently emphasized her belief that maintaining current interest rate levels will further decrease inflation, but she considers it premature to start reducing these rates.
Bowman plans to keep a close eye on upcoming economic data to determine the best course for monetary policy. She highlighted several factors that could potentially increase inflationary pressures. These include the effects of geopolitical conflicts, easing financial conditions, and the continued tightness in the labor market.
Bowman, in her prepared speech for the Florida Bankers Association, indicated that if data shows inflation steadily moving towards the Fed’s 2% target, there might be a case for gradually lowering the policy rate. However, she believes that time has not yet arrived. Her stance reflects a cautious approach to changing monetary policy, reiterating the importance of not acting hastily to decrease interest rates. Such premature action might lead to the need for future rate increases.
Bowman’s views on monetary policy echo her earlier statements this month, where she stated her readiness to increase the federal funds rate if future data suggests that inflation is not decreasing as expected or starts to rise again. Her comments underscore her commitment to achieving a 2% inflation rate over time, even if it means adjusting rates upwards in the future.
In terms of banking regulation, Bowman repeated her recommendation for substantial changes to a proposal made in July, which would require banks to boost their capital levels. She expressed concerns about proposals to reduce the maximum fees banks and payment companies can charge merchants for debit card transactions. Additionally, she critiqued the current official stance on bank mergers.
Bowman also suggested that improvements should be made to make the Federal Reserve’s discount window more efficient. This window is a tool used by the Fed to lend money to banks, playing a crucial role in maintaining stability in the financial system. Her comments highlight her broader focus on both monetary policy and banking regulation, aiming to ensure economic stability and control inflation.